
Education loans play a pivotal role in India by serving as a crucial financial tool that facilitates access to quality education. In a country where the cost of higher education is steadily rising, education loans have become indispensable for students aspiring to pursue advanced studies. In this Blog, “What are types of Educational Loan in India” we will do an in-depth analysis about Education loan in India.
What Is Education Loan?
An educational loan is a financial instrument specifically designed to assist individuals in funding their education expenses. Typically offered by banks, financial institutions, or government bodies, educational loans cover a wide range of educational pursuits, including tuition fees, books, accommodation, and other related costs.
The significance of educational loans lies in their ability to bridge the financial gap between the cost of education and an individual’s financial resources.
These loans enable individuals to overcome financial barriers and pursue their academic aspirations, irrespective of their economic background. Importantly, education loans contribute to the nation’s human capital development by ensuring that talented students are not deterred by financial constraints.
Significance of Education Loan in India
in a country as diverse and dynamic as India, access to quality education is crucial. As the cost of education continues to rise, many students and their families turn to education loans as a means to bridge the financial gap.
1) Financial Accessibility: The primary significance of education loans lies in providing financial accessibility to students who aspire to pursue higher education. With the escalating costs of tuition fees, accommodation, and other related expenses, many deserving students find it challenging to afford quality education. Education loans serve as a lifeline, enabling students to pursue their academic ambitions without compromising on the quality of education and to handle surprises (financial surprises) which can disturb their financial planning.
2) Inclusive Higher Education: Education loans contribute significantly to making higher education more inclusive. They break down financial barriers, allowing students from various economic backgrounds to access the same educational opportunities. This inclusivity is vital for fostering diversity and ensuring that talent is recognized and nurtured irrespective of financial constraints.
3) Investment in Human Capital: From an economic perspective, education loans can be seen as an investment in human capital. When individuals are equipped with quality education, they become valuable assets to the nation’s workforce. Education loans empower students to invest in their skills and knowledge, making them better prepared to contribute to the economic growth and development of the country.
4) Skill Development and Innovation: Education loans not only cover tuition fees but also facilitate skill development and innovation. Students can use the funds to attend workshops, conferences, and engage in extracurricular activities that enhance their overall learning experience. This, in turn, contributes to a more dynamic and innovative society.
5) Flexible Repayment Options: Many education loan schemes come with flexible repayment options, considering the financial circumstances of the borrowers. This flexibility eases the burden on students as they transition from education to employment, allowing them to establish themselves in their chosen fields without the immediate pressure of repaying the loan.
6) Boost to the Education Sector: The availability and utilization of education loans contribute to the overall growth of the education sector. Educational institutions benefit from increased enrollment, better infrastructure, and enhanced academic facilities, creating a positive cycle of development.
7) Empowering Women and Minorities: Education loans also play a crucial role in empowering women and minority communities by providing them with the means to pursue higher education. This empowerment contributes to a more diverse and inclusive workforce, fostering social equality and breaking down traditional barriers.
Types of Educational Loans in India
Education loans based on location
In the realm of education loans, one crucial factor to consider is the location of the educational institution – whether it’s domestic or abroad. This decision not only impacts the overall cost of education but also plays a pivotal role in shaping the terms and conditions of the loan.
Domestic Education Loans: For students opting to pursue education within their home country, domestic education loans become a primary financial resource. These loans are tailored to meet the specific needs of students studying at local universities and colleges. Here are some key features of domestic education loans:
1) Interest Rates: Domestic education loans generally come with lower interest rates compared to loans for international education. The interest rates may vary based on factors such as the lending institution, loan amount, and the borrower’s creditworthiness.
2) Collateral Requirements: In many cases, domestic education loans may not require collateral for smaller loan amounts. However, for larger sums, especially for professional courses, lenders may request collateral or a co-signer.
3) Repayment Period: The repayment period for domestic education loans is often more flexible. Lenders may provide longer repayment terms, making it easier for graduates to manage their finances after completing their studies.
4) Government-Sponsored Schemes: Government-sponsored education schemes with favorable terms for students pursuing higher education domestically are in existence. These schemes often provide subsidized interest rates and extended repayment periods, for example: Pradhan Mantri education scheme & Pradhan Mantri Vidya Lakshmi Karyakram.
International Education Loans: On the other hand, for students venturing abroad for their studies, international education loans become a vital financial lifeline. These loans are specifically designed to cater to the unique challenges and expenses associated with studying in a foreign country. Here are some key aspects of international education loans:
1) Higher Interest Rates: International education loans typically come with higher interest rates compared to their domestic counterparts. This accounts for the increased risk associated with lending for education in a foreign country.
2) Collateral Requirements: Due to the higher loan amounts involved, international education loans often require collateral or a co-signer. This ensures the lender’s security, especially when dealing with borrowers who may not have a credit history in the host country.
3) Currency Exchange Risks: Borrowers taking international education loans face the added challenge of currency exchange fluctuations. The loan amount is disbursed in the currency of the host country, and any devaluation of the borrower’s home currency could increase the repayment burden.
4) Specialized Loan Providers: Many financial institutions specialize in offering international education loans. These lenders understand the unique needs of students studying abroad and provide services tailored to those requirements.
Education loans based on Different level of education
Undergraduate Education:
a. Professional Courses: Education loans for undergraduate professional courses such as engineering, medicine, law, and management are widely available. Financial institutions often consider the reputation of the educational institution, course duration, and potential future earnings of the student when determining loan eligibility and terms.
b. General Undergraduate Courses: For non-professional undergraduate courses, including arts, science, and commerce, the loan terms may vary. Interest rates could be influenced by factors such as the institution’s accreditation, the academic performance of the student, and the co-applicant’s financial stability.
Postgraduate Education:
a. MBA and Management Programs: Management programs, especially Master of Business Administration (MBA), are popular choices for postgraduate education. Education loans for these programs often come with competitive interest rates and flexible repayment options, considering the potential for higher future income.
b. Technical and Specialized Courses: Postgraduate technical and specialized courses, such as M.Tech, M.Sc, and PhD programs, are also eligible for education loans. The loan amount may cover tuition fees, examination fees, and even additional expenses like research-related costs.
Vocational and Skill Development Programs:
a. Short-Term Courses: Vocational and skill development courses have gained prominence due to their focus on employability. Education loans for such courses may be available, though the loan amount and terms might differ from traditional academic programs.
b. Certification Programs: Financial institutions may offer education loans for certification programs in areas like digital marketing, data science, and cybersecurity. These loans often prioritize the practical relevance and industry demand for the chosen certification.
Study Abroad Programs:
a. Global Education Loans: Aspiring students seeking education abroad can also benefit from education loans tailored for international studies. These loans consider factors such as the destination country, course reputation, and potential for global career opportunities.
b. Foreign Exchange Programs: Some institutions offer financial support for students participating in foreign exchange programs. These loans may cover travel expenses, tuition fees, and other associated costs during the exchange period.
Education loans based on with or without Collateral
Secured Education Loans:
Loan Against Property (LAP): In this type of education loan, borrowers provide collateral in the form of property to secure the loan. The interest rates are generally lower compared to unsecured loans.
Loan Against Fixed Deposit (FD): Some banks offer education loans against fixed deposits held by the student’s family. The FD serves as collateral, making it a secured loan.
Unsecured Education Loans:
Personal Loans for Education: Unsecured personal loans are another option where no collateral is required. However, interest rates for these loans are usually higher, and the loan amount may be limited.
Government-sponsored Education Loans:
SBI Education Loan Scheme: The State Bank of India (SBI) offers education loans for various courses, both in India and abroad. The interest rates are competitive, and repayment terms are flexible.
Central Sector Interest Subsidy (CSIS): Under this scheme, the government provides interest subsidy during the moratorium period for students from economically weaker sections.
Educational Institutions-linked Loans:
Institution-specific Loans: Some educational institutions collaborate with banks to offer special loan schemes for their students. These loans may have specific terms and conditions tailored to the institution’s requirements.
Government backed or private educational loans
Government-Backed Education Loans: Government-backed education loans in India are typically offered by banks and financial institutions in collaboration with government schemes. Some well-known government-backed education loan schemes include the State Bank of India (SBI) Education Loan Scheme, Vidya Lakshmi Portal, and the Central Government Interest Subsidy Scheme.
Pros of Government-Backed Education Loans:
Lower Interest Rates: Government-backed loans often come with lower interest rates compared to private loans, making them more affordable for students.
Collateral-Free Loans: Many government-backed schemes offer loans without the need for collateral, making it easier for students from economically weaker backgrounds to secure funding.
Repayment Grace Period: These loans typically have a moratorium period during the course and a specified grace period post-education before the repayment begins.
Interest Subsidy Schemes: Some government-backed loans come with interest subsidy schemes, reducing the overall financial burden on the borrower.
Cons of Government-Backed Education Loans:
Stringent Eligibility Criteria: Government-backed loans may have strict eligibility criteria, limiting access for some students.
Bureaucratic Processes: The application and approval process for government-backed loans can be time-consuming and bureaucratic.
Private Education Loans: Private education loans in India are provided by various private financial institutions and banks. These loans are designed to cater to a broader spectrum of students, offering flexibility in terms of eligibility and loan amounts.
Pros of Private Education Loans:
Flexible Eligibility: Private loans may have more flexible eligibility criteria, making them accessible to a wider range of students.
Quick Approval: Private education loans often have a faster approval process, allowing students to secure funds more quickly.
Customized Loan Amounts: Private lenders may provide higher loan amounts, covering not only tuition fees but also additional expenses like accommodation and living costs.
Cons of Private Education Loans:
Higher Interest Rates: Private education loans usually come with higher interest rates compared to government-backed loans, resulting in a higher overall repayment amount.
Collateral Requirement: Many private lenders may require collateral, making it challenging for students without assets to secure a loan.
Limited Grace Periods: Private loans may have shorter grace periods, leading to a quicker start of the repayment phase after completion of studies.
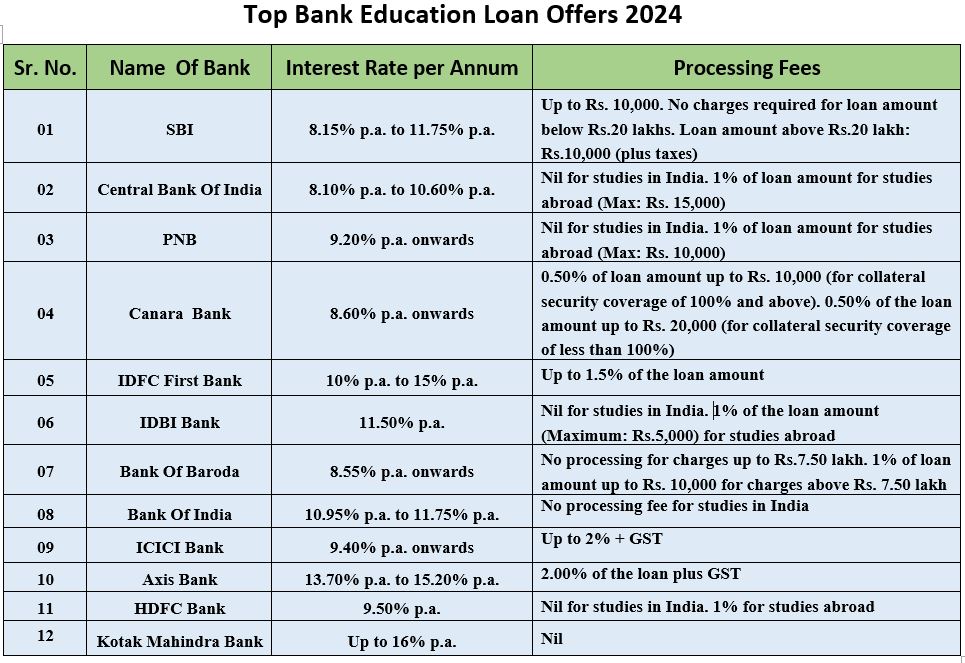
Disclaimer: Banks can have fixed or fluctuating interest rates. These fluctuating interest rates changes with the Repo Rate. The above mentioned interest rates are effective as of January 2024 and are subject to change as per the bank’s rules and regulations.
Eligibility Criteria for an Education Loan
The eligibility criteria for education loans in India may vary slightly among different banks and financial institutions, but generally include the following:
1) Age Limit: The applicant should be between 16 and 35 years of age. However, some banks may extend the upper age limit.
2) Educational Qualification: The applicant should have secured admission to a recognized course in India or abroad.
3) Course Eligibility: The education loan typically covers courses like undergraduate, postgraduate, professional, and vocational courses. The courses should be offered by recognized institutions.
4) Co-applicant: Most banks require a co-applicant, who is usually a parent, guardian, or spouse. The co-applicant’s income and creditworthiness are considered during the loan approval process.
5) Creditworthiness: Both the applicant and co-applicant must have a satisfactory credit score. A good credit history increases the chances of loan approval.
6) Collateral: Depending on the loan amount, banks may ask for collateral. For loans above a certain threshold, tangible assets like property, fixed deposits, or government securities may be required as security.
7) Margin Money: Some banks may ask for a margin amount, which is a percentage of the total cost of the course. The applicant or co-applicant needs to contribute this amount, and the loan covers the remaining cost.
8) Repayment Period: The repayment period usually begins after the completion of the course. The borrower is given a certain grace period to find employment before starting the repayment.
9) Income Proof: The co-applicant needs to provide income proof, such as salary slips, income tax returns, or bank statements, to demonstrate the ability to repay the loan.
10) Admission Letter: The applicant needs to provide the admission letter from the educational institution as proof of enrollment.
11) Expense Details: The applicant must provide a breakdown of the course-related expenses, including tuition fees, examination fees, hostel charges, cost of books, etc.
12) Insurance: Some banks may require the borrower to take out an insurance policy to cover the loan amount in case of unforeseen events.
Documents Required for Education Loan
All banks and loan giving private bodies have their set of document requirements. However, most of the loan giving bodies generally have some common document requirements as mentioned below:
- Admission or Offer Letter from the institute.
- Loan Application form
- Residence Proof
- Identity Proof
- Academic records
- Cource cost details
- Documents of Collateral (if required)
- Bank Statement
- Income Proof
- If Required Co-Borrower’s documents
- Guarantor documents (if required)
Tax Benefits on Education Loan
According to section 80E of Income Tax Act of 1961, the interest which a person payes on student loan can be deducted. However, this tax deduction advantage is available only for individual borrowers and can be only considered for the purpose of higher education.
This deduction can be availed for study in all fields, (domestically as well as internationally). It includes both vocational and academic courses.
The point to taken into consideration is that tax deduction is applicable only to the interest portion of the EMI, and not on the principle. However, no limit is prescribed to how many times one can claim this benefit. To get the claim, You requires a certificate from your financial organization/bank that segregates the principal and interest components of your EMI.
This benefit is accessible for eight years from the day you start repaying your loan or until the interest component is paid off, whichever comes first.
Below is an informative video explaining the in and outs of an education loan. Hope this will exhance the understanding.
Challenges and Solutions
Education is often considered a gateway to success, but the rising costs of tuition and other associated expenses have led many students to explore educational loans as a means to fund their academic pursuits. While educational loans provide a lifeline for aspiring students, they come with their own set of challenges.
Common Challenges Faced by Loan Applicants
1) Stringent Eligibility Criteria: One of the primary challenges faced by education loan applicants is the stringent eligibility criteria set by financial institutions. Students may find it difficult to meet the necessary conditions, especially if they lack a credit history or a co-signer with a strong financial standing.
2) High Interest Rates: Educational loans often come with high-interest rates, which can significantly increase the overall repayment amount. This can pose a burden on students, particularly in the initial years of their careers when they may be facing financial constraints.
3) Limited Loan Amounts: Financial institutions may cap the loan amount, leaving students with insufficient funds to cover all their educational expenses. This limitation can force students to seek alternative means of financing, potentially compromising the quality of their education.
4) Repayment Periods: The relatively short repayment periods for educational loans can create pressure on borrowers, especially when they are just starting their professional journeys. The looming prospect of repayment can affect career choices and hinder personal and professional growth.
Tips for Managing Educational Loan Repayments
1) Budgeting and Financial Planning: Developing a comprehensive budget and financial plan is crucial for successful loan repayment. This involves tracking income, expenses, and allocating a specific portion of income towards loan repayment.
2) Early Career Planning: Students can strategically plan their careers to maximize income potential early on. Identifying high-demand industries and acquiring relevant skills can enhance job prospects and ease the burden of loan repayment.
3) Loan Refinancing: Exploring loan refinancing options can be beneficial, especially if lower interest rates or more favorable repayment terms are available. However, borrowers should carefully consider the terms and conditions before opting for refinancing.
4) Utilizing Grace Periods: Many educational loans offer a grace period before repayment begins. Utilizing this time to secure stable employment and financial stability can provide a solid foundation for loan repayment.
Loan Default and Consequences
1) Impact on Credit Score: Failing to meet loan repayment obligations can have a severe impact on the borrower’s credit score. A lower credit score can hinder future financial endeavors, including obtaining other loans or credit cards.
2) Legal Consequences: Persistent loan default may lead to legal actions by lenders to recover the outstanding amount. This could include wage garnishment, asset seizure, or other legal measures to reclaim the funds.
3) Limited Financial Opportunities: Defaulting on an educational loan can limit financial opportunities for individuals. It may affect the ability to secure housing, employment, or pursue further education.
Frequently Asked Questions

- What procedure to be followed for an education loan without collateral?
Procedure includes filling the application form, compiling latest documents as per the checklist from the financial institution these details will be submitted to the bank officials. Upon verification it will be send to the processing centre. After Processing officer verification and approval (upon meeting the eligibility requirements) bank sanctions the loan. After the loan is sanctioned, you will be required to sign the documents. Loan amount will be transferred to the related account. - Which banks gives an education loan without collateral?
In India, public as well as private banks give higher education loan without collateral. The difference comes in the amount for loan. Also option of getting a loan from NBFCs is also there, which works same as private bank. Some of the banks giving unsecured loan are: SBI, BOB, Axis, ICICI, Avanse, Incred etc. - What are the different collateral types that students can consider for loan application?
Different collateral types can be your flats, your house, non-agricultural lands (Some financial institutions consider Agricultural lands also), life insurance, fixed deposits, government bonds etc.
Additional Resources
Click here to apply for education Loans from State Bank Of India
Click here to apply for education loan from Union Bank Of India
Click here to apply for education loan from Bank Of Baroda
Click here to get the details of Education loan from leading banks of India
Click here to apply for education loan from HDFC Bank
Central Sector Interest Subsidy (CSIS)
Conclusion
In conclusion, education loans play a pivotal role in facilitating access to quality education in the Indian context, bridging the financial gap for aspiring students. The numerous benefits of education loans, including lower interest rates, flexible repayment options, and tax benefits, make them an attractive financial aid option for those pursuing higher studies. However, careful consideration of key factors such as interest rates, repayment terms, and eligibility criteria is essential to ensure that borrowers make informed decisions.
In the Indian scenario, where the cost of education is rising, education loans significantly contribute to empowering students to pursue their academic aspirations, fostering a more inclusive and educated society. As education remains a cornerstone for personal and societal growth, the significance of education loans cannot be overstated in India’s dynamic educational landscape. Hope this blog, “What are types of education loan in India”, has met its purpose of sharing good information.
